Who needs an ELF code?
An ELF Code is a subset of identifiers based on the Legal Entity Identifier. ELF (Entity Legal Form) refers to the type of entity that an organisation may be, such as a Limited Company, Fund Trust and there is a list of over 3,250 entity legal types across 175 countries listed on the GLEIF Entity Legal Forms list. Other examples of ELFs are:
- LLC
- Limited liability partnership (LLP)
- Gesellschaft mit beschränkter Haftung (GmbH)
- Société Anonyme (SA)
- Fund
Each jurisdiction has its own definition of entity types such as Limited companies, and the LEI acts as a master identifier for all legal entity types, using the ELF code as secondary identifier.
Similar to an LEI, but shorter (4 characters in total) the ELF code is an alpha-numberic code that will often appear on an LEI record allowing the viewer to determine the type of entity they are looking at.
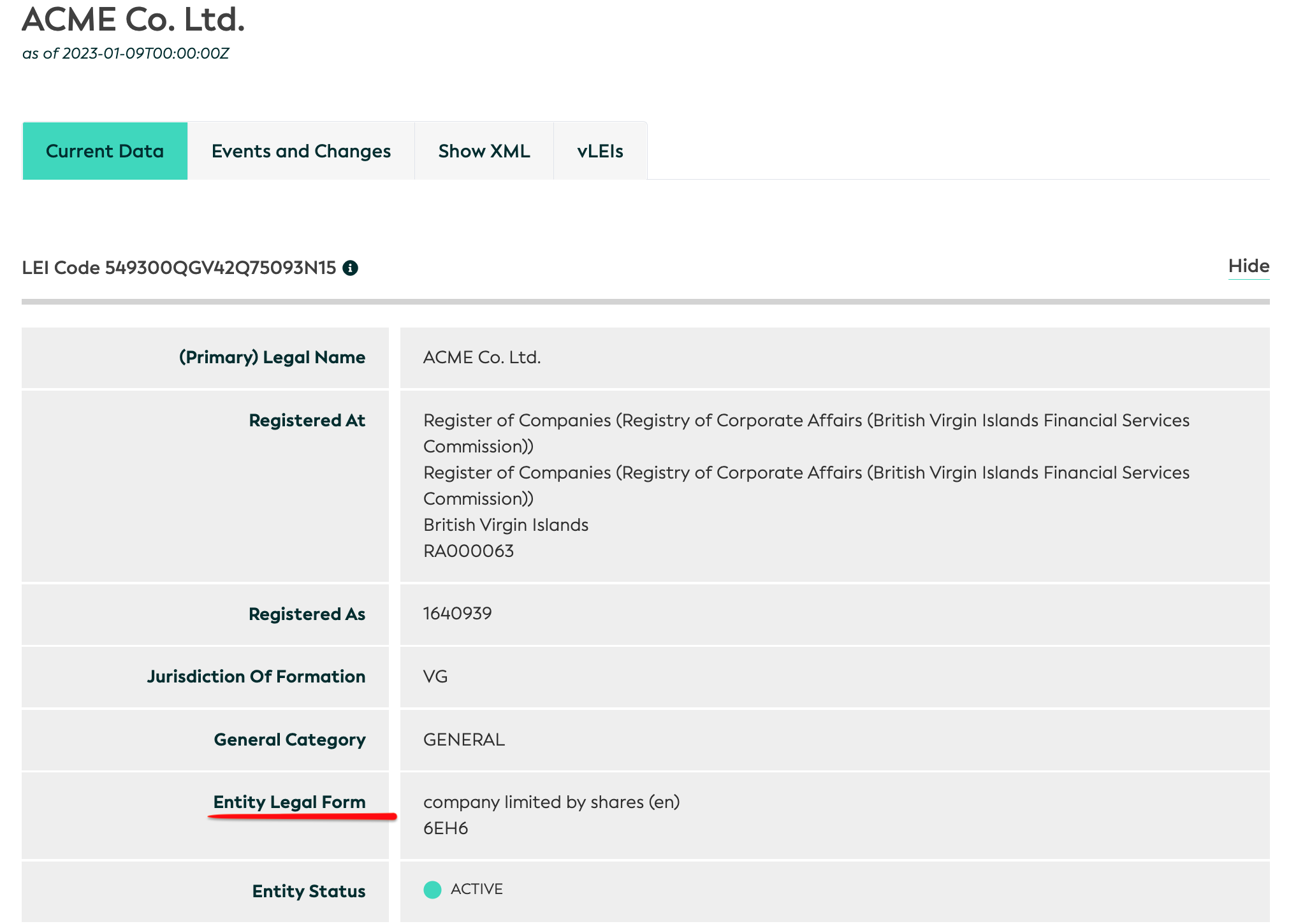
By checking an LEI using the LEI Search Tool, you will be able to view its ELF code. Below you can see an example. This company's ELF code is 6EH6, which is a British Virgin Islands company limited by shares.
ISO 20275: Entity Legal Forms Code List
The ELF code, like the LEI code, is an ISO standard in its own right. Not different to an LEI in so far as an ISIN code is, but a sub-set of the LEI standard. Established in 2017, the ISO state that the ELF code:
“specifies the elements of an unambiguous scheme to identify the distinct entity legal forms in a jurisdiction. Its aim is to enable legal forms within jurisdictions to be codified and thus facilitate the classification of legal entities according to their legal form”.
Understanding the type of entity is an important piece of data when considering a legal entity within financial services, not only for regulators, but also for legal entities to consider with whom they are conducting business.

As the LEI is becoming more heavily mandated across all industries, we can see its benefits as it touches all parts of the compliance value chain. The ELF code plays no small part in helping users of LEI data distinguish what type of entities are players in their jurisdictions, in an easy to read, standardised and machine readable format.
According to the ISO, the ELF code:
- enables unique identification globally of entity legal forms
- defines an ELF scheme that is reliable and an ELF Code that is persistent;
- defines an ELF code that contains no embedded intelligence regarding the identification of the entity legal form to which it applies;
- leverages the expertise of ISO/TC 68 in defining and maintaining identifier standards;
- defines an ELF scheme that is extensible and free from limitation on use and redistribution.
ELF CODES: USE CASES
As the LEI and the benefits of voluntary adoption begin to become more widely recognised, some interesting new use cases are emerging.
A recent EU-wide inventory of citizens engaging in energy actions (e.g generation of energy through renewable sources) for the past 20 years has been recorded with data from almost 30 EU countries, and 10,000 initiatives.
To date, these initiatives have lacked a cross-country database. Now with a massive compilation of data a new database has been formed allowing for easier statistical and data analysis on the sector.
The initiative have used the #GLEIF Entity Legal Form (ELF) codes to identify entity types covered in the initiative in a unique, and clever way of mapping "who is who" within the project. These entities are mostly Friendly Societies, with no legal form, or Sustainable Energy Communities. However the LEI services as a 'master identifier' allowing for one common way of identifying all participants.
GLEIF, GLEIS and the LEI (Legal Entity Identifier)

What is an LEI?

LEIConsolidate - Bulk Transfer LEIs

LEI Costs & Prices

The LEI and the Compliance Value Chain

USA LEI Regulations
